Biomechanical Assessment
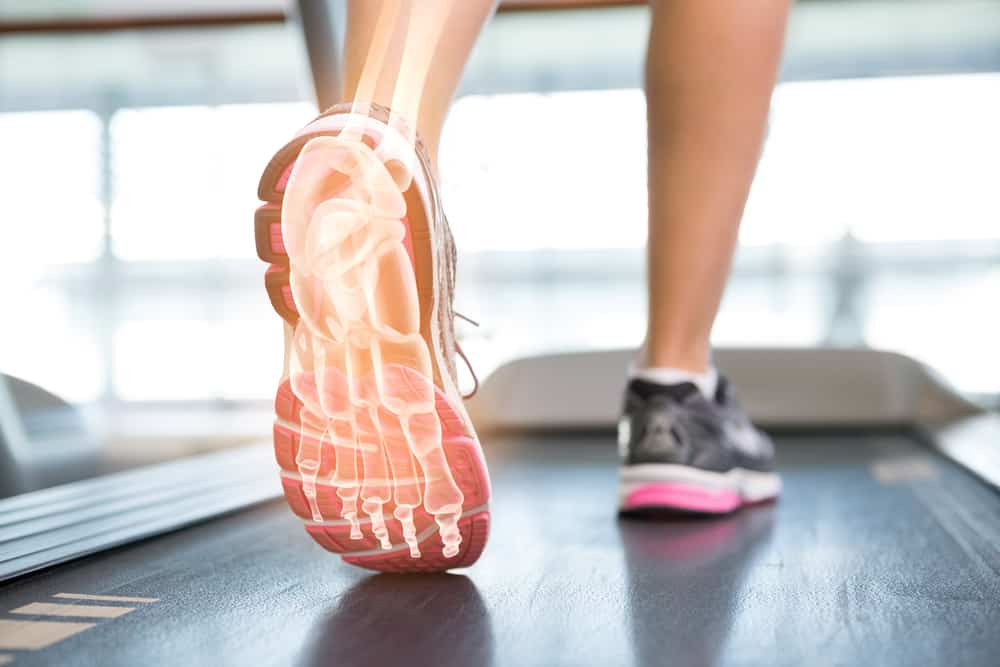
Biomechanical Assessment
is an examination of your feet, legs, hips and general structure to see how it relates to your walking pattern. The podiatrist will take detailed measurements and look for any irregularity which may contribute to pain or abnormalities in these areas. This will provide a comprehensive understanding of any underlying problems in the lower limbs. Our Biomechanical assessments take an hour and a half as we look at the posture of the body under a range of different circumstances including Static/Dynamic, weight bearing/non-weight bearing modes.
Biomechanical problems include:
- Painful feet
- Knee pain
- Back pain
- Hip pain
- Ankle pain or discomfort in the ball of the foot
- Flat feet
- Strain on the Achilles tendon and Plantar fascia ligament
- Injuries
For more information please use the toggle switches below:
Flat feet, Pes Planus or fallen arches is a common problem which may occur in up to 20% of adults. Pes Planus is the loss of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot. This can be flexible or rigid, resulting in flattening of the plantar surface. The condition may be congenital, developmental or acquired through illness, injuries or musculoskeletal problems. Generally treatment is only needed if the condition is recent, painful, progressing, or when there is a fixed bony deformity.
Pes Planus can be part of normal development and is probably genetic. 45% of children aged 3-6 years have a flat medial longitudinal arch. Many babies are born with what appears to be ‘flat feet’ but it cannot be properly diagnosed until all the bones, muscles, ligaments and tendons have properly grown and developed. Most children develop a normal longitudinal arch by the age of 10.
Pes planus is not a serious condition and may only cause pain when children are running.
Foot arches add elasticity and flexibility to the foot and absorb shock during gait. Collapse of the medial longitudinal arch force the feet to pronate which can stress the soft tissues leading to tendinopathies and nerve entrapment. Flattened arches can also cause micro-tears in the spring ligament and plantar fascia, leading to Plantar fasciitis and heel spurs. Pes Planus may also cause bunions and metatarsalgia. Poor posture may eventually develop, which can lead to back, neck, hip and knee pain.
Causes of Pes Planus in Children :-
- Ligamentous laxity
- Obesity in children
- Neurological problems – eg, cerebral palsy, polio.
- Bony abnormalities
Causes of Pes Planus in Adults:-
- Posterioral Tibial Dysfunction
- Tear of the spring ligament
- Tibialis anterior rupture
- Chronic injuries
- Neuropathic foot caused by diabetes, polio, or other neuropathies.
- Age-related degenerative changes in foot and ankle joints:
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis.
- Fractures.
- Bony abnormalities – eg, tarsal coalition.
- Other bony abnormalities such as rotational deformities, tibial abnormalities, fusion of tarsal bones, equinus deformity.
- Ligamentous laxity
- Footwear which limits toe movement like high heels
- Tight Achilles tendon or calf muscles may cause pes planus.
- Obesity alters gait
- Pregnancy can cause flattening of the foot arches
- Hip abductor weakness
- Knock knees
Treatment in children :-
Paediatric treatment ‘flexible pes planus’ is controversial as the condition tends to improve with age. Few paediatric flat feet are symptomatic and therefore do not require treatment.
Customised orthoses should be reserved for:-
- Children with foot pain and arthritis.
- Unusual morphology.
- Unresponsive cases to conservative treatments.
Surgery is only indicated in children when Pes planus is symptomatic and rigid.
Treatment in adults :-
- Fixed Pes planus, surgery may be required.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories.
- Orthotics Surgery.
Diagnosis is normally from clinical examination or biomechanical assessment. The evaluation provides both static and dynamic information which is then used to fabricate custom made orthotics which will stabilise the foot and improve posture and gait. If Pes planus is flexible, bilateral, painless, and is not progressing, it does not require treatment.
Pes cavus or a cavoid foot, is characterized by a high arch of the foot that does not flatten with weightbearing. Pes cavus is common, occurring in approximately 10% of the population. It can also be a sign of an underlying neurologic disorder such as ‘Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease’.
Claw toes and trigger hallux are often associated with a high arched foot because the extensor tendons are tight due to the shape of the foot. This increases pressure on the metatarsal heads and can lead to metatarsalgia, corns, calluses and plantar fasciitis.
Types :-
- Congenital / genetic- may be derived from family.
- Neuromuscular diseases – may affect nerves and muscles.
- Diabetic neuropathy-Charcot
- Trauma – severe foot trauma through fractures and burns
Pes cavus can cause excessive Supination which is outward rolling of the foot and ankle due to a very high arch. Lateral ankle sprains, hip, knee and back pain are common problems.
Symptoms :-
- Foot Drop
- Imbalance / Instability of the foot
- Pain in the metatarsal heads
- Frequent lateral ankle sprains
- Hammertoes
- Pain while walking / standing
- Stiffness in the lower leg and foot joints
- Overall foot pain
- Claw Toes
- Sesamoid Pain
- Achilles tendonitis
- Hip, knee and back pain
- Painful corns and calluses
Treatments :-
- Stretching exersises
- Orthotics to improve ground contact of the plantar surface of the foot and reduce supination.
- Shoe modifications.
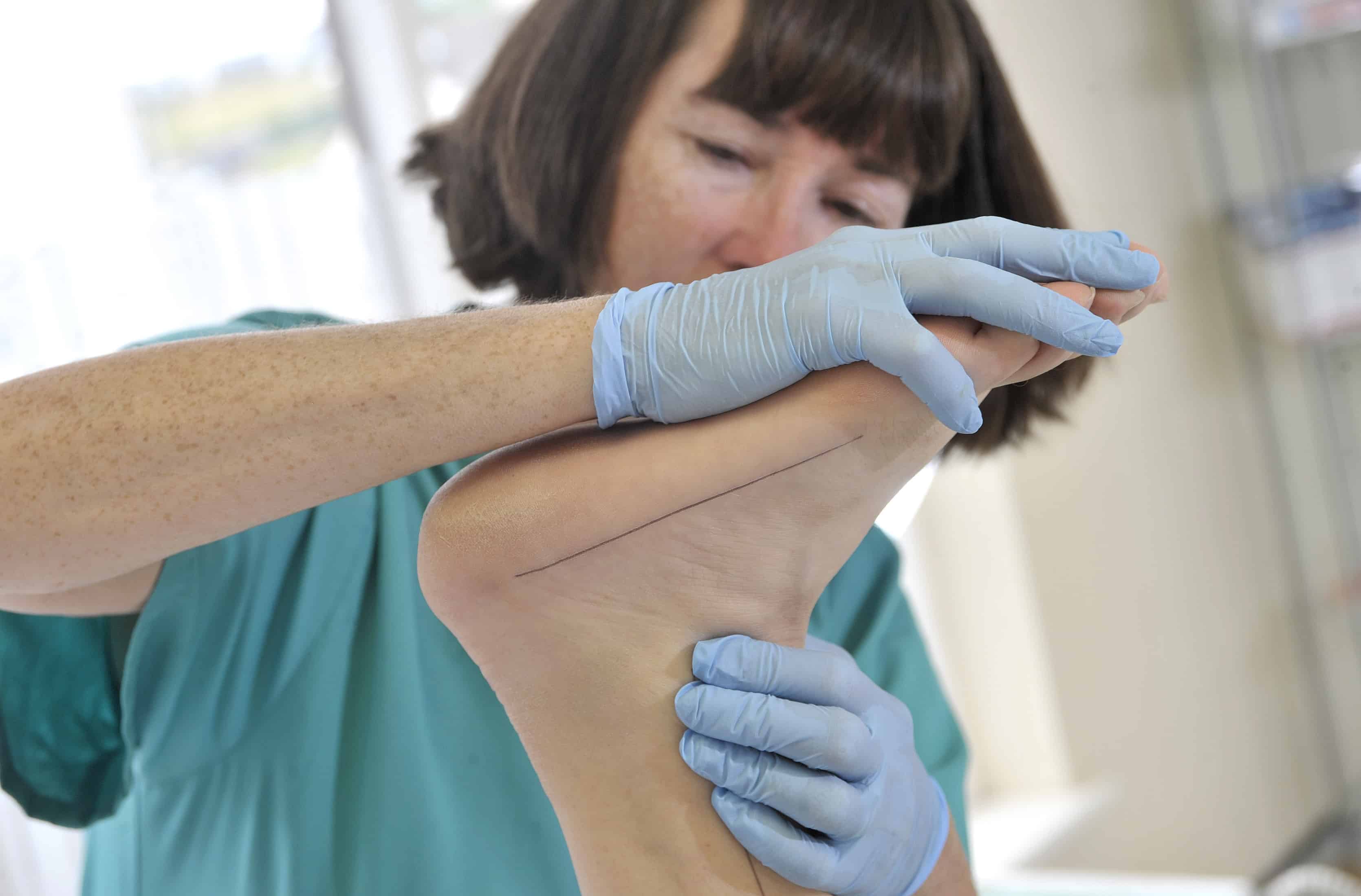
A Biomechanical Assessment provides a comprehensive understanding of any underlying problems in the lower limbs, looking at how your feet function when you stand or move and if the way they are functioning leads to pain in the feet, knees, hips or back.
This involves an examination of the lower limbs, looking at their structure, alignment, strengths and weaknesses and the relationship between them. It is important to examine the lower limbs as a whole because they are closely connected and pain in one area can be due to a weakness or problem in another. The podiatrist takes a full medical history, then examination of the joint range and motion of your hips, knees and feet. Muscle strength and weaknesses will also be assessed and the podiatrist will look for any signs of limb length discrepancy, examining the structure of the foot and looking at the relationship between the forefoot and rear foot.
This evaluation provides both static and dynamic information which can then be used to create a personal treatment plan which may include exercises or custom made orthotics to treat the condition, however sometimes simple changes such as wearing trainers designed for your gait or wearing insoles can be effective. For people who have good structural foot mechanics the podiatrist may only need to advise upon the best footwear in order to reduce your symptoms and help to prevent further symptoms from arising.
For those with more serious underlying problems the information from the examination can be used to fabricate custom made orthotics, or in very serious cases, referral to a podiatric surgeon.
Appointments take a good hour, Please wear shorts or loose fitting trousers and bring your everyday footwear, sporting footwear and Orthotics if you already use them.
For the treatment of :-
- Heel pain
- Forefoot pain
- Ankle Pain
- Achilles, Peroneal Tendinitis
- Shin splints
- Exercise induced leg pain.
- Hip pain.
- Knee pain.
- Lower back pain.
Also useful in the treatment of :-
- Children with walking abnormalities or pain
- Injuries which have not responded to other treatments
- Professional and recreational athletes prone to injury.
- Diabetics
Most health insurances will pay for a biomechanical assessment and orthotics but you should check with your particular policy before commencing treatment.
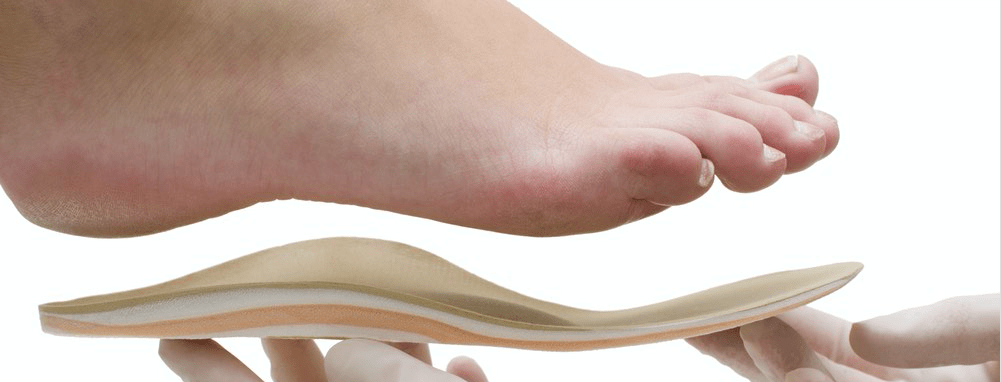
Orthotics are specialized insole devices that correct or modify how the foot functions. By keeping the foot properly aligned they can redistribute the weight placed on the foot to change its function, protect the foot, or both.
Pain occurs when the foot is not functioning correctly. Orthotics can help solve a number of biomechanical related problems. They can reduce pain, not only in the foot, but in other parts of the body such as the knee, hip and lower back. In addition they can increase stability in an unstable joint. Furthermore they can prevent a deformed foot from developing additional problems and as a result improve overall quality of life.
Orthotics range from simple insoles to offload painful corns and callus. Semi bespoke over the counter devices. However we mainly prescribe bespoke custom made orthotic from a full biomechanical assessment.
Over the counter orthotics
Over the counter orthotics are available and can help people with minor symptoms however they cannot correct a wide range of symptoms.
Custom made orthotics
Custom made orthotics, in which a mould is made of your foot ,so that the orthotics work precisely with your uniquely individual foot structure are the most effective. Orthotics are specially created in a laboratory. These correct misalignments and deformities so that when they are placed in your shoes your feet are perfectly aligned.
Different types of material are used to construct custom made orthotics depending upon the patients needs.
Rigid orthotics
Rigid orthotics are designed to control function and are mainly used for walking or dress shoes. They control motion in the two major foot joints that lie directly below the ankle joint and are usually made of a firm material such as plastic or carbon fibre. Rigid orthotics are designed to improve or eliminate strains, aches and pains in the legs, thighs and lower back.
Soft orthotics
Soft orthotics help absorb shock, increase balance and take pressure off painful areas. They are effective for patients with diabetes, arthritis, or deformed feet. Soft custom made orthotics are usually made of soft, cushioned materials so that they can be worn against the sole of the foot, extending from the heel past the ball of the foot together with the toes and will protect the feet from stress.
Semi-rigid orthotics
Semi-rigid orthotics help correct foot balance for walking or participating in sports. They are typically made of layers of soft material reinforced with rigid materials for support. They are often used by athletes to reduce pain when they train and compete.
Appointments take a good hour, Please wear shorts or loose fitting trousers and bring your everyday footwear, sporting footwear and Orthotics if you already use them.
For the treatment of :-
- Heel pain
- Forefoot pain
- Ankle Pain
- Achilles, Peroneal Tendinitis
- Shin splints
- Exercise induced leg pain.
- Hip pain.
- Knee pain.
- Lower back pain.
Also useful in the treatment of :-
- Children with walking abnormalities or pain
- Injuries which have not responded to other treatments
- Professional and recreational athletes prone to injury.
- Diabetics
Most health insurances will pay for a biomechanical assessment and orthotics but you should check with your particular policy before commencing treatment.