Common Foot Problems
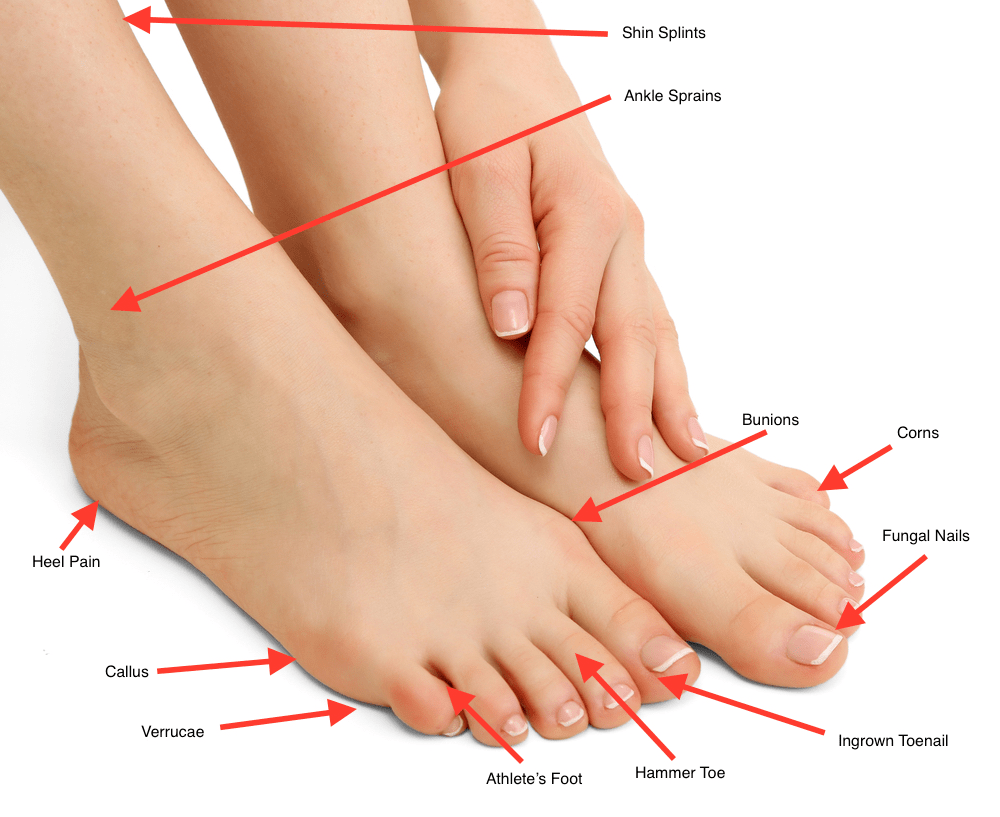
For more information on the common foot problem treatments that are available, please use the toggle switches below:

Athletes Foot or Tinea Pedis is a name given to a fungal infection of the feet, caused by fungi growing and multiplying on the skin. It occurs primarily between the toes, but can be anywhere on the foot, and can affect anyone, not just athletes. If left untreated it can spread to other parts of the foot and sometimes spreads to the toe nails, causing Fungal Toenails. It can manifest in a number of different ways depending on the type of fungi that is present on the skin. Athletes Foot between the toes looks white and soggy usually where there is excessive moisture. Sometimes the skin will split and will become itchy and smelly.
Athletes Foot can be extremely uncomfortable, causing the skin surrounding the area to become inflamed and swollen, sometimes containing sticky fluid. People suffering from this condition may also experience a scaly rash on the underside of their foot , causing cracks in the skin.
Other areas of the feet such as the soles may become affected by different types of fungi appearing as blisters or flaky dry skin. Caught in damp environments such as gyms changing rooms and shower floors the fungi that cause the infection thrive in warm, dark and moist places.
Symptoms :-
- Dry, itchy lesions
- Burning, itching or stinging sensation between the toes
- Itching, red, dry, scaly and flaky on the soles
- Blisters on the feet that itch
- Sticky fluid between the toes
- Rash, or cracks on the underside of the foot
- Often people with athletes foot can also develop fungal nail infections
- If left untreated, this condition can become very painful
- Discoloured, thick, crumbly toenails that become detached from nail bed
Causes :-
Anyone can develop this condition, though it is more common in people with sweaty feet, as the fungi thrive in warm, moist environments. Many people can have the fungus present on their feet but are not affected by it however cracks or abrasions allow fungus to enter the skin, consequently symptoms then develop.
Athletes foot can be spread around your body, if you scratch your feet it can spread to your hands. It is also contagious and can easily spread to other people by touching infected skin or coming into contact with contaminated surfaces or objects. You are more prone if you have a weakened immune system or health conditions such as diabetes. Athletes foot can also cause the skin to split between the toes leading to a bacterial infection and in severe cases cellulitis, which causes the foot to become red, hot and swollen.
Prevention :-
- Keep your feet clean and dry, particularly the between your toes
- Wearing cotton socks and roomy shoes made of natural materials
- Change your socks and stockings every day
- Alternate your footwear to allow them to dry out
- Do not walk barefoot in public areas
- Do not share towels, socks, shoes
- Applying surgical spirit between toes to stop them getting sweaty
- It is important not to use moisturiser between your toes, as this can help fungi multiply
Treatments :-
Athlete’s foot is unlikely to get better on its own. It can usually be treated using anti-fungal treatments from pharmacies. Treatment should aim to control moisture and perspiration whilst also treating the infection with the appropriate drugs and topical remedies.
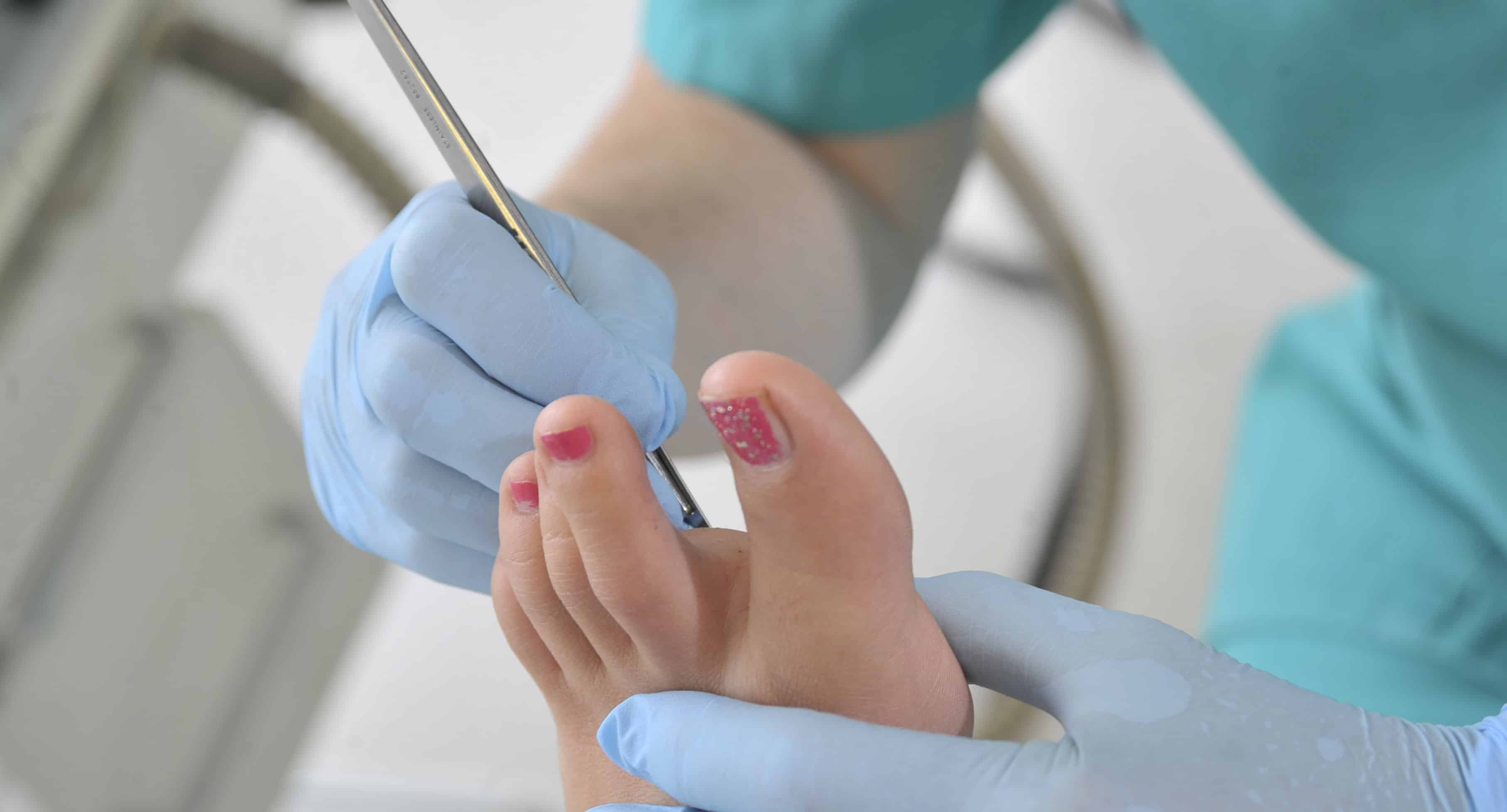
A corn is a small concentrated area of hard skin usually conical in shape which presses on the underlying nerve endings and can cause severe pain.
Caused by pressure from your shoes or the ground surface, they can be found anywhere on the foot particularly where the joints are prominent such as hammer toes.
The shape of the foot may increase pressure along with various activities or occupations that require long hours of standing , inappropriate footwear and poor foot function.
Over the counter remedies, usually in the form of corn plasters, come in two varieties:-
- Foam rings which try to reduce the pressure on the corn.
- Medicated corn plasters which often contain an acid which aims to soften and dissolve the corn. There is a risk with this type that the liquid may dissolve healthy skin if not applied precisely consequently this may not only be painful but in the case of diabetics and those with poor circulation, very dangerous.
It is very important not to leave corns unchecked if they are neglected they may become inflamed and in severe cases ulcerated.
A Podiatrist can remove corns using a scalpel which is a painless procedure.
A callus is a larger area of hard skin but has no central nucleus like a corn. If calluses become too thick they often produce an unpleasant burning sensation particularly if on the ball or heels of the feet.
Caused by pressure and friction which may be aggravated from ill fitting footwear, foot shape, occupation and biomechanical problems within the feet.
Treatment is painless removal of excessive callus using a scalpel and providing instant relief.
Other methods may involve using appropriate padding insoles or orthotics. Your Podiatrist will advise on the best options for you.

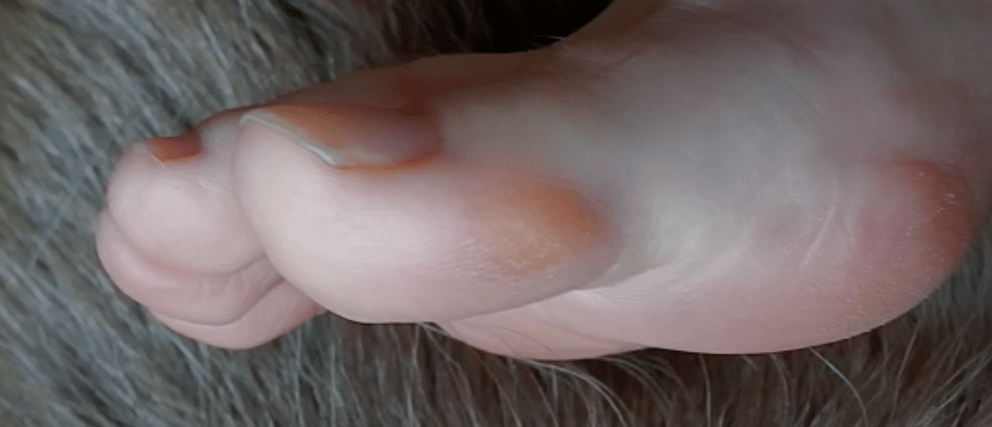
Cracked heels or heel fissures are caused by excessively dry skin. The drier the skin becomes the less elasticity it has causing it to tear into an open wound. It is often described as walking on glass. Most heel fissures are only superficial because the upper layer of the skin known as the epidermis is involved. In severe cases it will affect the next layer of skin or the dermis and this is when fissures become deep and painful.
Skin fissures may appear anywhere on the body but the most common area is around the rim of the heel or other parts of the feet that are exposed to the elements and prone to developing callus.
Working in very wet and damp conditions can also make the skin water logged and this can also cause fissures.
Cracked heels are not harmful unless they become painful or infected.
Fissures are a common foot complaint and can affect a person at any age.
Causes:-
Naturally dry skin i.e hereditary tendency.
Heavy callus
Inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis
Low grade fungal infection.
Diabetes and hypothyroidism (under active thyroid).
Exacerbated by:-
Prolonged standing on hard surfaces.
Weight gain
Open foot wear, sandals or flip flops
Climate or environment
Self help for cracked heels :-
Dry cracked heels
Soaking feet in warm water regularly. Dry skin thoroughly and use abrasive foot file to debride rough skin. Then apply a urea based foot balm. This will help to retain some of the moisture after bathing. Foot balms are best applied once or twice daily. Some people find that scraping the hard skin off when the skin is dry is more effective than doing it after a soak. If feet have a low grade fungal infection a broad spectrum anti fungal cream will help.
Wet cracked heels
Expose feet to open air as much as possible. Apply an astringent such as surgical spirit as it helps to dry skin. Wear foot wear and socks made with natural materials if able to.
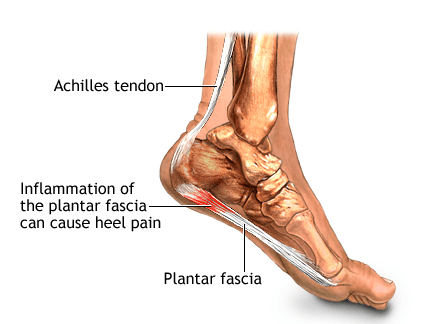
Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain, hence approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year. It occurs when the strong band of tissue that supports the arch of your foot becomes irritated and inflamed. The plantar fascia is a long, thin ligament that connects the heel to the front of your foot.
Plantar Faciitis can be very painful and can be felt as a dull ache with episodes of a sharp pain in the heel or under the arch. The pain is often worse in the morning or after periods of rest and improves during the day.
Causes :-
The plantar fascia is designed to absorb the high stresses and strains we place on our feet, However, sometimes, too much pressure damages or tears the tissues. The body’s natural response to injury is inflammation, which results in heel pain and stiffness of plantar fasciitis.
In most cases, plantar fasciitis develops without a specific, identifiable reason. There are, however, many factors that can make you more prone to the condition:
- Tight calf muscles that make it difficult to flex your foot
- Weight gain
- Flat feet
- Very high arch
- Repetitive impact activity (running/sports)
- New or increased activity
- Footwear
- Injury
Heel Spurs
Although many people with plantar fasciitis have heel spurs, spurs are not the cause of plantar fasciitis pain.
One in 10 people may have heel spurs, but only 1 in 20 people with heel spurs have foot pain. Because the spur is not the cause of plantar fasciitis, the pain can be treated without removing the spur.
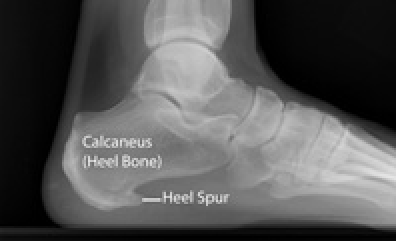
X-ray of heel spur
Diagnosis is normally from patient history and clinical examination, the Podiatrist will discuss the best course of action to relieve symptoms.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Primarily we treat this condition conservatively as this is less invasive and the patient is less likely to suffer side effects and complications than more invasive methods.
90% of patients may improve within 10 months of starting simple treatment methods.
Rest
Decreasing or even stopping the activities that make the pain worse is the first step in reducing the pain. You may need to stop athletic activities where your feet pound on hard surfaces (for example, running or step aerobics).
Ice
Rolling your foot over a cold water bottle or ice for 20 minutes is effective. This can be done 3 to 4 times a day.
Oral Medication
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen or naproxen reduce pain and inflammation.
Exercise
Plantar fasciitis is aggravated by tight muscles in your feet and calves. Stretching your calves and plantar fascia is an effective way to relieve the pain.
Orthotics
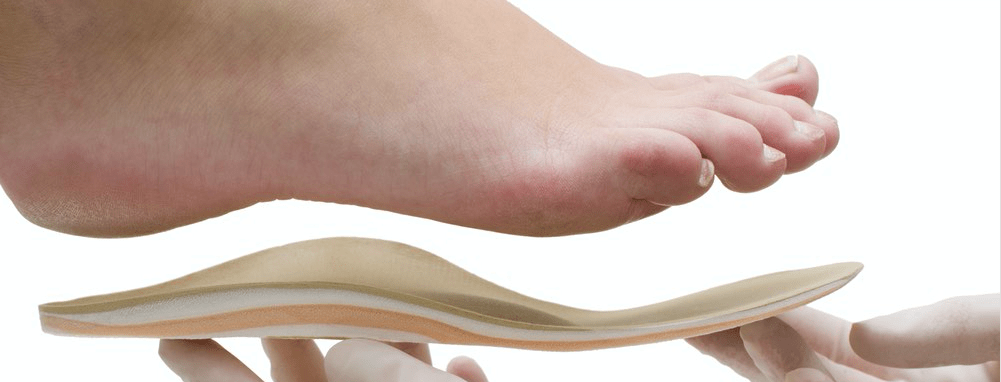
A biomechanical assessment will provide both static and dynamic information which is then used to fabricate custom made orthotics this will relieve the stress on the plantar fascia.
Low Level Laser
Low level laser therapy is effective in reducing the pain and inflammation and will accelerate the healing.
Other treatments may include night splints or a steriod injection.
For more information click here
Foreign bodies are objects such as glass thorns and hairs that become embedded in the feet and may cause considerable irritation infection and pain until the object has been removed.
The body may be able to eliminate superficial small particles that have become trapped just below the skins surface. However sometimes larger ones that are quite deep may require surgical removal by a Podiatrist.
Metatarsalgia is a general term for pain in the ball of the foot consequently there can be several reasons why the symptoms appear.
Forcing the feet into narrow restrictive footwear such as high heels squeeze the metatarsal heads together. This can cause damage to various soft tissues such as the ligaments nerves and joint capsules. Correspondingly sets up inflammation making it very difficult to walk.
Other causes are high impact sports that can cause stress fractures in this area of the foot. Particularly if the appropriate footwear for a type of sport have not been worn during the activity.
Diagnosis is usually from clinical examination or biomechanical assessment and the Podiatrist will discuss the best course of action to relieve the symptoms.
LLLT has been effective in healing the damaged tissues and orthotics may be recommended if there is an underlying biomechanical problem.
Flat feet, Pes Planus or fallen arches is a common problem which may occur in up to 20% of adults. Pes Planus is the loss of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot. This can be flexible or rigid, resulting in flattening of the plantar surface. The condition may be congenital, developmental or acquired through illness, injuries or musculoskeletal problems. Generally treatment is only needed if the condition is recent, painful, progressing, or when there is a fixed bony deformity.
Pes Planus can be part of normal development and is probably genetic. 45% of children aged 3-6 years have a flat medial longitudinal arch. Many babies are born with what appears to be ‘flat feet’ but it cannot be properly diagnosed until all the bones, muscles, ligaments and tendons have properly grown and developed. Most children develop a normal longitudinal arch by the age of 10.
Pes planus is not a serious condition and may only cause pain when children are running.
Foot arches add elasticity and flexibility to the foot and absorb shock during gait. Collapse of the medial longitudinal arch force the feet to pronate which can stress the soft tissues leading to tendinopathies and nerve entrapment. Flattened arches can also cause micro-tears in the spring ligament and plantar fascia, leading to Plantar fasciitis and heel spurs. Pes Planus may also cause bunions and metatarsalgia. Poor posture may eventually develop, which can lead to back, neck, hip and knee pain.
Causes of Pes Planus in Children :-
- Ligamentous laxity
- Obesity in children
- Neurological problems – eg, cerebral palsy, polio.
- Bony abnormalities
Causes of Pes Planus in Adults:-
- Posterioral Tibial Dysfunction
- Tear of the spring ligament
- Tibialis anterior rupture
- Chronic injuries
- Neuropathic foot caused by diabetes, polio, or other neuropathies.
- Age-related degenerative changes in foot and ankle joints:
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis.
- Fractures.
- Bony abnormalities – eg, tarsal coalition.
- Other bony abnormalities such as rotational deformities, tibial abnormalities, fusion of tarsal bones, equinus deformity.
- Ligamentous laxity
- Footwear which limits toe movement like high heels
- Tight Achilles tendon or calf muscles may cause pes planus.
- Obesity alters gait
- Pregnancy can cause flattening of the foot arches
- Hip abductor weakness
- Knock knees
Treatment in children :-
Paediatric treatment ‘flexible pes planus’ is controversial as the condition tends to improve with age. Few paediatric flat feet are symptomatic and therefore do not require treatment.
Customised orthoses should be reserved for:-
- Children with foot pain and arthritis.
- Unusual morphology.
- Unresponsive cases to conservative treatments.
Surgery is only indicated in children when Pes planus is symptomatic and rigid.
Treatment in adults :-
- Fixed Pes planus, surgery may be required.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories.
- Orthotics Surgery.
Diagnosis is normally from clinical examination or biomechanical assessment. This evaluation provides both static and dynamic information which is then used to fabricate custom made orthotics which will stabilise the foot and improve posture and gait. If Pes planus is flexible, bilateral, painless, and is not progressing, it does not require treatment.
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a systemic auto immune disease affecting multiple joints throughout the body.
Usually symptoms appear in several joints on both feet first and include pain, swelling, stiffness and muscle weakness. Bony changes can often lead to misalignment or partial dislocation of the joints.
You may develop corns, bunions, claw toe or hammer toe as a result.
The earlier it’s diagnosed, the more effective your treatment. Don’t ignore joint pain, as Rheumatoid Arthritis often shows up in the feet first.
Diagnosis is normally from clinical examination and medical history. The Podiatrist will discuss the best course of action to relieve the symptoms which may include referral for blood tests or X-rays.
Primarily we treat this condition conservatively as this means the patient is less likely to suffer side effects of more invasive treatments.
A biomechanical assessment may be necessary. This can then used to fabricate custom made orthotics to relieve the pain by redistributing the pressure away from the joints.
LLLT is also effective in reducing the pain and inflammation and reducing the need for painkilling drugs.
For those who have not had any success with less invasive methods surgery may be recommended. The most successful option being fusion in which the bones are fused resulting in a loss of movement in that particular joint which can reduce pain.
For more information click here

A bunion is a bony deformity at the base and side of the big toe joint. The big toe moves towards the other toes and may also rotate and twist.
Wearing shoes that are too tight may accelerate the development and cause irritation and inflammation around the joint. They are usually hereditary and linked to genetics. Foot injuries and flat feet that pronate also may contribute.
Bunions can also lead to secondary problems, such as hammertoe, corns, calluses, ulcers, bursitis and arthritis.
Many people with bunions suffer from discomfort and pain from the constant irritation, rubbing, and friction of the joint against shoes, consequently the bigger the bunion gets, the more it hurts to walk.
Because they are bony deformities, bunions do not resolve by themselves.
Our objective is minimum invasive treatment initially as this is less hazardous and the patient is less likely to suffer side effects and complications of more invasive methods.
A Podiatrist will remove the corns and calluses gently with a scalpel and can advise on the best form of treatments available which may also include protective padding, orthotics, or splints for night time wear ( this is often recommended for adolescents with bunions, because their bone development may still be adaptable ).
Low Level Laser Therapy is also effective in reducing pain.
In severe cases where these conservative methods have failed referral to a specialist surgeon may become necessary.