Diabetes
Diabetes is a disease characterised by abnormally high levels of glucose in the blood.
There are two types, but ultimately the condition has similar effects on the body.
- Type 1 diabetes is when the body stops producing insulin due to the destruction of the cells in the pancreas.
- Type 2 diabetes is when the pancreas is not producing enough insulin or the cells are not responding. Insulin is the hormone produced by the pancreas and controls the amount of glucose in the blood.
It is needed for the glucose to enter our cells and supply the body with energy but without it the glucose stays in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is more common than type 1. 90% of all adults in the UK will have type 2.
People with Diabetes are at a higher risk of developing problems with their feet. Diabetes may impair blood flow and sensitivity of your feet, you may not feel extremes of temperatures or pain and as a result problems may occur without you even knowing. The skin can also become dry due to automatic nerve neuropathy increasing the likelihood of problems as diabetes affects the rate of healing and so breaks in the skin can take longer to heal.
If you suffer from Diabetes you must pay particular attention to your foot health. Good diabetic control means fewer complications. It is important to inspect your feet on a daily basis and you should have your feet professionally examined at least once a year. A Podiatrist can perform vascular, neurological and function tests which will monitor your foot health status. Early intervention and treatment is crucial to avoiding serious foot problems. Diabetes can cause serious damage to the eyes, kidneys, heart, blood vessels, nerves.
Market Street Clinic undertake all diabetic foot care, including neurovascular assessments (checking pulses and sensation). For more information please feel free to send us a message or to book an appointment please call 01566 777600.
For more information on the diabetes treatments that are available, please use the toggle switches below:
Many of the problems diabetic people have with their feet are caused by pressure from ill fitting footwear. They may range from corns & calluses to open sores and infection. However, if the blood vessels and nerves in the feet become damaged due to persistently high glucose levels over a long period of time it can lead to more serious complications as people are often unaware that anything is wrong.
Foot problems associated with Diabetes:-
- Corns, & calluses
- Athletes foot on skin &/ or nails
- Yeast infections on skin & nails
- Thickened toe nails
- Excessively dry cracked skin
- Bacterial infection from ingrown/ involuted toe nails, cuts, grazes & ulcers
Peripheral neuropathy:-
- Tingling, pins & needles
- Hypersensitivity to temperature &/or slightest touch
- Pain &/or Parasthesia
- Complete loss of sensation
- Charcot foot
Impaired circulation:-
- Faint or absent pulses
- Brittle discoloured toe nails that don’t grow very well
- Dusky red/purplish thin,shiny fragile skin
- Open painful sores around the peripheries of the foot & tips of toes
- Infection
- Gangrene
How to take care of your feet and advice on when to get professional help.
Diabetes can reduce the blood supply to your feet and cause a loss of feeling known as peripheral neuropathy. This can mean foot injuries do not heal well, and you may not notice if your foot is sore or injured.
If you have diabetes, you are 15 times more likely to have a limb Amputated due to gangrene.
Foot care tips if you have diabetes
- Podiatry foot checks at least once a year.
- Keep your feet clean and free from infection.
- Wear shoes that fit well and don’t squeeze or rub. Ill-fitting shoes can cause corns and callouses, ulcers and nail problems.
- Never walk barefoot, especially in the garden or on the beach on holidays.
- Cut or file your toenails regularly.
- Get corns or hard skin treated by a Podiatrist.
- Seek treatment from your GP or Podiatrist if foot blisters or injuries do not heal quickly. Treat ulcers urgently, within 24 hours, especially if there is redness or swelling around the area, or in an area where you’ve previously been warned to seek immediate attention.
If you have diabetes, it’s important to stop smoking. Smoking impairs the blood circulation, particularly in people with diabetes. It can seriously worsen foot and leg problems.
You should see your doctor urgently if:-
- you notice breaks or discharge in the skin of your foot.
- the skin on your foot changes colour and becomes more red, blue, pale or dark
- you notice extra swelling in your feet where there was a blister or injury
- An unpleasant smell from your foot.
For more information click here
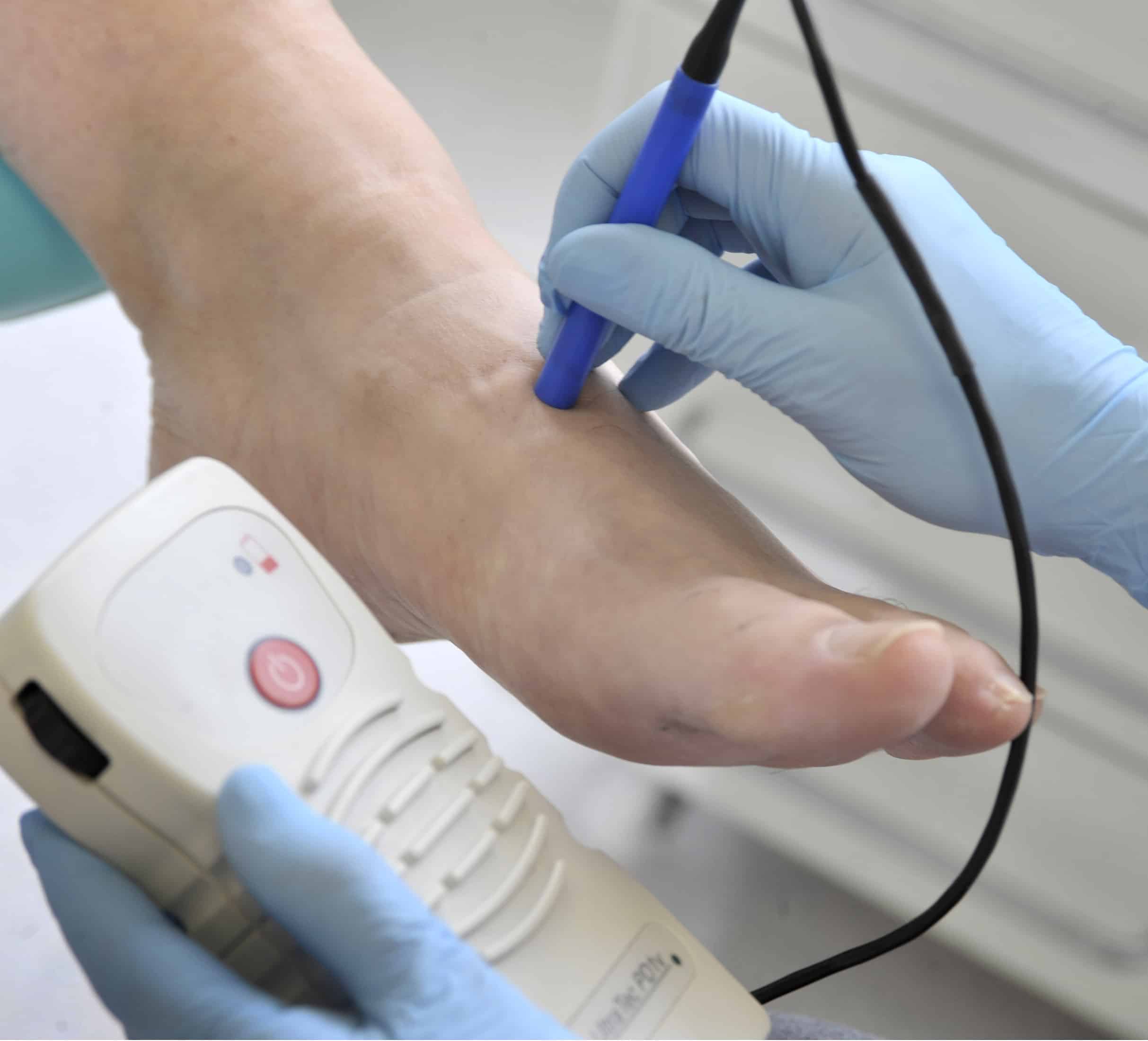
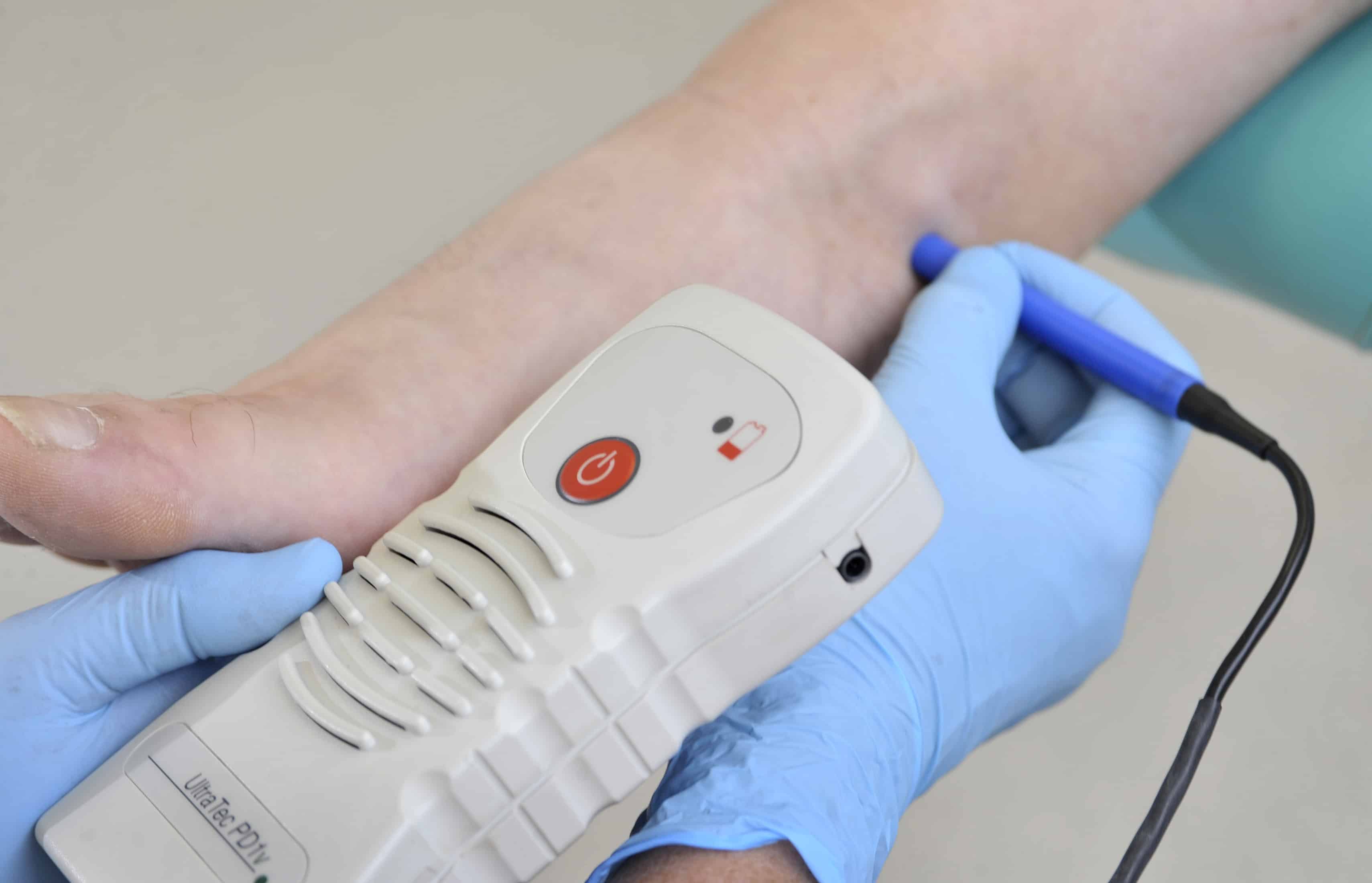
Diabetic foot Screening involves tests to see if a patient is at risk of ulceration. If they are, then they ought to be assessed.
A diabetic assessment with a Podiatrist involves a sequence of vascular, neurological and functional tests to assess the level of risk. These include tests with a retractable monofilament for pressure and sensation, palpation of foot pulses, medical history and a visual check on the skin for dryness, cracks, heel fissures and skin temperature. Circulation can be checked and Neuropathy measured.
The purpose of the assessment is to look for altered sensation and impaired circulation. Any other routine foot problems can be dealt with such as care of nails, corns and callus. Podiatrists are experts at relieving pressure from areas of the feet that are at risk of ulceration.
Neurological assessment:-
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common cause of diabetic foot ulceration. The clinical examination of the foot is designed to identify loss of protective sensation in various areas of the foot.
Your Podiatrist should perform a complete foot inspection at least annually but more often if you have foot problems.
Contact your Podiatrist if you have cuts or breaks in the skin, or have an ingrown nail, changes in color, shape, or if your foot just feels different (less sensitive or hurts).
If you have corns or calluses, your Podiatrist can remove them for you and also trim your toenails if you cannot do so safely.
Circulatory Assessment :-
- Palpating pulses in feet
- Observing colour & general appearance of skin & nails
- Using doppler if pulses are weak or absent
- Looking for ulcers, infection & gangrene
Caring for Your Feet :-
- Check your feet daily. Look at your bare feet for red spots, cuts, swelling, and blisters. If you cannot see the bottoms of your feet, use a mirror or ask someone for help.
- Wear Orthopaedic footwear if advised by your Podiatrist
- Wash your feet every day. Dry them carefully, especially between the toes.
- Keep your feet soft and smooth.
- If you can see and reach your toenails, trim them when needed.
- Wear shoes and socks at all times.
- Never walk barefoot.
- Wear comfortable shoes that fit well and protect your feet.
- Protect your feet from hot and cold.
- Wear shoes at the beach or on hot pavement.
- Don’t put your feet into hot water.
- Never use hot water bottles, heating pads, or electric blankets.
- Don’t smoke.
- Set a time every day to check your feet.
Tinea Pedis is a fungal infection that usually starts on the skin and sometimes spreads to the toe nails. It can manifest in a number of different ways depending on the type of fungi that is present on the skin.
Atheletes Foot commonly appears between the toes and the skin looks white and soggy usually where there is excessive moisture. Sometimes the skin will split and will become itchy and smelly.
Other areas of the feet such as the soles may become affected by different types of fungi appearing as blisters or flaky dry skin. In severe cases it can spread to the toenails.
Caught in damp environments such as gyms changing rooms and shower floors.
Treatment should aim to control moisture and perspiration whilst also treating the infection with the appropriate drugs and topical remedies.